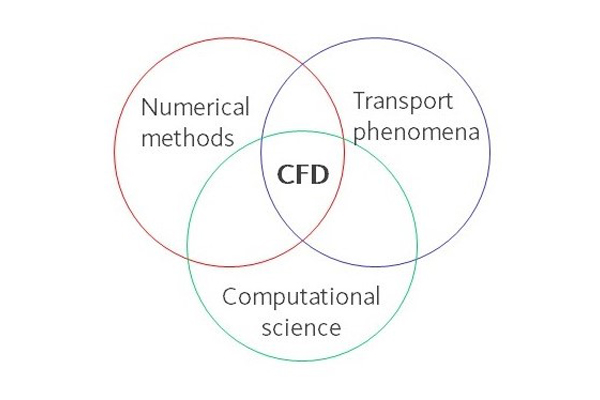
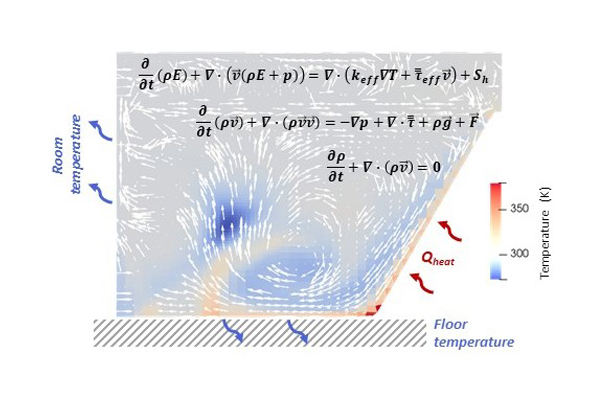
CFD is the combined use of partial differential equations, numerical methods and computing sciences. It allows for solving complex systems in three or two spatial dimensions and time with the highest accuracy.
The computing cost of a CFD simulation is usually high, so it cannot be directly used for real-time monitoring purposes.
Software: OpenFOAM – Ansys.
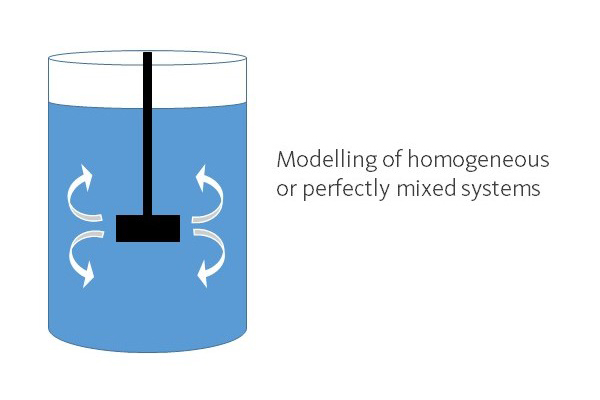
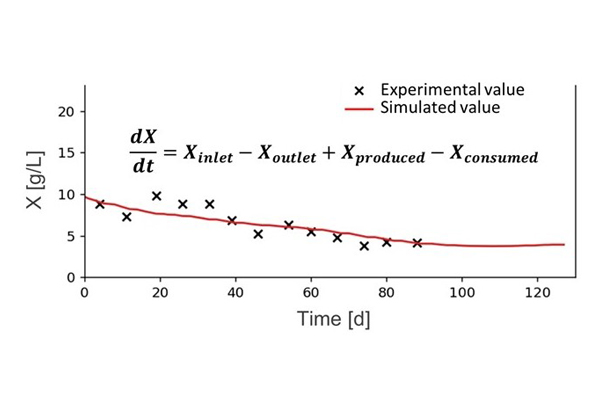
ODEs capture the temporal changes of a system, assuming its spatial homogeneity. It allows for understanding the dynamic evolution of several compounds or species that take part in a (bio)chemical process.
The computing cost of an ODE system is not high, so it can be directly used for real-time monitoring purposes.
Software: Matlab – Python
This approach involves techniques searching for correlations within a data set, without considering the underlying fundamental principles that govern the specific process.
Permite procesar una gran cantidad de datos de diferentes categorías de sistemas que son difíciles de modelar de otro modo.
Software: Python.



Hybrid modeling comprehensively combines CFD, EDO and Machine Learning techniques. In this approach, mechanistic models (CFD/EDO) generate volumes of high-quality data to calibrate and validate Machine Learning models, ensuring their robustness and reliability. Additionally, we develop simplified ODE-based models optimized for real-time execution.
These are fed by detailed CFD simulations, which, due to their high computational demand, are processed asynchronously. This architecture allows us to offer precise and agile solutions for the supervision and control of industrial processes.